
Given that the number and severity of cyber-attacks and crimes are increasing over time, the importance that users and companies place on their information security has multiplied. Firewalls are one of the important security equipment used to protect the network and system against external access.
Firewalls have been developed with the aim of filtering or blocking malicious traffic or data. A network that is not equipped with powerful firewalls is always at risk of hacker threats, and the security and stability of its systems are minimized.
If you acquire the necessary information about different types of firewalls and how they work, in addition to understanding the role of this security shield, you can ensure that your network or system remains with a top-grade firewall. This article is for How Has My Website Been Hacked?
What is a firewall?
When it comes to secure access to data and computer system operations, a firewall is the first thing that comes to mind. If we want to define a firewall in the simplest possible way, we should say:
“A firewall is a type of filter between the computer system and the internet, which protects the computer system by providing access to the permitted and healthy content of the internet and blocking malicious and dangerous content.”
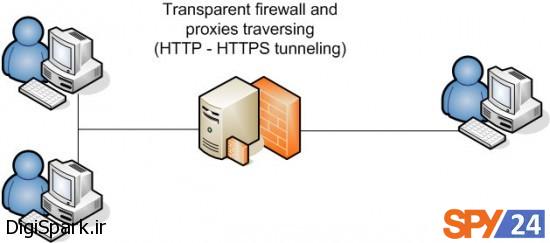
Firewalls – as an important part of network security – began operating in the late 1980s, and over time, with the increase in cyber threats and attacks, they have made significant progress in order to have the necessary power to protect the system and counter all kinds of viruses, attacks, and threats.
Given that a firewall prevents unauthorized access to the network through software or firmware, the equivalent of this scenario in the real world would be erecting a fence around valuable assets located in a house.
A firewall can be a hardware, software, or cloud unit that identifies incoming and outgoing network traffic according to a set of specific rules in order to prevent cyber attacks by filtering certain accesses at the appropriate time. However, it is worth mentioning that firewalls can provide different levels of protection, and the key is to determine how much protection you need.
Without a firewall, the idea of the internet would have faded shortly after its inception. So, we conclude that the web world becomes meaningful with the concept of a firewall.
Uses of a firewall
Using a firewall affects the performance and security of computer systems in various ways, and we will refer to the most important of them below:

1) Preventing unwanted content
There are no restrictions on the presence of unauthorized and unwanted content on the internet. Such content can easily infiltrate the system unless it is equipped with a strong firewall. Most operating systems have a firewall that handles this filtering well.
2) Preventing remote unauthorized access
Many hackers are operating in cyberspace today and are constantly trying to gain access to vulnerable systems. Banking organizations and national security agencies value the security of confidential data more than any other organization. A strong firewall prevents hackers from gaining remote access and protects sensitive data, transactions, and so on.
3) Ensuring security based on protocol and IP address
Hardware firewalls are useful for examining traffic activities based on a specific protocol. When a connection is established, the activity path is tracked from start to finish to avoid jeopardizing the system’s status.
4) Maintaining the integrity of organizational operations
Today, most organizations are dependent on software and organizational systems, and thanks to decentralized distributed systems with the ability to access data from anywhere in the world, authorized users have access to these systems and can work on them.
So, a user, upon receiving the necessary credentials and permissions, can enter the system and access their desired data. Therefore, a large organization with sensitive and important data needs a strong firewall to maintain its integrity and ensure security in all aspects.
5) Protecting private conversations
Organizations that enter service industries must constantly interact with their customers. This interaction takes place with various goals and methods, such as meetings, interviews, and chats. The content exchanged in these interactions is confidential, and any leakage damages the trust of customers and, consequently, the credibility of the organization. Using a firewall protects the system, and the secure flow of information gives customers a sense of reassurance.
Other uses of this security unit include the following:
- Preventing access to obscene and unethical content (especially for children and teenagers)
- Keeping a history of events for identifying patterns and improving rules to keep up with threats
- Use in antivirus applications
- Preventing ransomware, malware, and phishing attacks
- Preventing damage to old PCs due to new operating systems
- Providing more security for gamers
- …
How do Firewalls Work?
A firewall operates based on a set of pre-determined rules about traffic, and after analyzing the nature of the traffic, it categorizes it as either permitted or unauthorized. These rules are considered based on several aspects, and any traffic that violates these rules is denied access to the system.

All firewalls filter operations using a combination of the following:
Source: The address of the system intending to connect to the network.
Destination: The address of the system to which the source system intends to connect.
Content: What kind of content is this connection trying to access or exchange?
Packet Protocols: What language this connection is using to transmit the message? Among the network protocols responsible for establishing communication between hosts, TCP/IP protocols are usually used for internet communications.
Application Protocols: Common protocols used in this context include HTTP, Telnet, FTP, DNS, and SSH.
In fact, a firewall is like a gatekeeper located at the system’s entrance point or port and only allows access to trusted sources and IP addresses that have successfully passed identification checks. For example, the address 172.18.1.1 can only access address 172.18.2.1 through port 22.
Consider IP addresses as house addresses and port numbers as rooms within the house. Only authorized people can enter the house. Then the filter intensity increases so that people inside the house only have access to specific rooms (ports). For instance, the homeowner is allowed to enter any room, while children and guests only have access to specific rooms.
Most firewalls examine data in four communication layers of the TCP/IP protocol, namely the application, transport, network, and data link layers (from top to bottom). These layers guide the movement of data from the source to the destination. The more advanced the network Firewall’s security technology, the possibility of examining higher layers is provided. The ability to gather more information with more advanced firewalls enables the system to provide more precise traffic controls.
Advantages of Using a Firewall
Understanding the benefits of using a firewall may make you pay more attention to the security of your business. Keep in mind that no matter how little your business relies on network technology, you should never ignore the protection of your data and your business as a whole. Let’s get acquainted with the advantages of firewalls – the first line of defense against external threats:

Network Traffic Monitoring
Being able to monitor incoming and outgoing network traffic and preventing damage before your system or server is affected by threats is a great advantage that using a firewall brings to you. The firewall operates based on predefined rules and filters to protect your system. This protection is carried out by examining incoming/outgoing packets through the network, and if the packet contains dangerous commands or data, the firewall detects it and immediately blocks it.
Protection Against Malware
Malware, especially trojans, is very dangerous for users. They silently enter the system and monitor all user operations and actions. The information they gather is sent to a web server, and unless they exhibit some strange behavior, you won’t even realize they’re present. So, what better idea than to take control of your system using a firewall and protect your system by timely blocking malware and virus attacks?
Prevention of Hacking
Hackers are active members of the internet world and are always looking for a system that they can illegally infiltrate and carry out their malicious activities. Therefore, the strongest weapon you can use against hackers is a strong firewall. If you properly set the firewall rules, rest assured that hacking attacks will be identified and stopped as soon as possible, preventing any unauthorized access to data, emails, systems, etc.
Access Control
With firewalls, you set policies for your system or server that control access to it. Given that some hosts and services are more vulnerable to hacking attacks than others if you control or entirely block access to such hosts on your system, your network security level increases.
Better Privacy Protection
Privacy is a major concern for users, and when hackers are constantly looking for clues about users, you should also think about increasing the level of privacy protection. With a firewall, the conditions for obtaining privacy details disappear. Also, if you are thinking about the privacy of your website users, you can take measures like blocking the DNS service and DNS system information to prevent hackers from accessing the domain and IP address of the system.
Types of Firewall
Firewalls are divided into several categories based on their structure and methods. Below, we examine each of these:

Packet-filtering firewall
Packet filtering is recognized as the most common and basic type of firewall. It functions by examining only the information present in packet headers, such as destination and source IP addresses, packet type, port number, and other superficial details, to decide whether they are allowed or not. They do not interfere with the packet contents. Therefore, if a packet with malicious content is sent from a trusted address, it is allowed into the system, which is considered a significant flaw. For example, if a valid address requests the deletion of a database, it receives system access due to its compliance with established rules, succeeding in deleting the intended database. Such situations limit the protective quality of this firewall, leaving the system more vulnerable.

This firewall is divided into four categories: Static, Dynamic, Stateless, and Stateful.
Static packet filtering firewall requires you to manually create rules. Therefore, rule definition, port management, access control lists (ACLs), and IP addresses are all performed by the user. Conversely, dynamic firewalls allow users to set rules dynamically to reflect specific conditions. You can adjust ports to stay open for specific time intervals and then automatically close. These firewalls offer greater flexibility than static ones because you can set specific parameters and automate certain processes.
Stateless firewalls examine packets independently of each other and become an easy target for hackers due to their disregard for the connection between sequential packets. In contrast, stateful firewalls remember information related to previously sent packets, which helps increase their security.
Overall, packet-filtering firewalls do not have much security, mainly due to their lack of packet content inspection. Using this firewall is a cost-effective solution to protect devices in an internal network and segregate internal traffic related to different network sectors.
However, Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) is another form of packet filtering that identifies, classifies, reroutes, or blocks data using specific barcodes. As previously mentioned, regular packet filtering only checks the header, but this firewall checks both the header and the packet contents.
Advantages:
- Fast and efficient for scanning traffic based on headers
- Does not use excessive resources
- Low cost
Disadvantages:
- Does not examine packet content
- Vulnerable to IP spoofing
- Inability to filter application layer protocols
Proxy Service Firewall
This firewall protects the network by filtering application layer messages and acts as a gateway from one network to another. The client must first send their request to the firewall, then the proxy firewall evaluates the nature of the message based on its own rules and decides whether it is allowed or not.
Another important point is that the proxy firewall controls layer 7 traffic of protocols such as HTTP and FTP, and by examining and processing packet contents with a combined method of DPI and stateful, it identifies malicious traffic.
This filtering method, in addition to checking IP addresses, ports, and core packet protocols (UDP and ICMP) like a packet-filtering firewall, also considers protocols like FTP, HTTP, DNS, etc., to allow for deeper inspection and filtering of many data properties.
Advantages:
- Excellent performance in hiding network structure and internal IP addresses
- Better security decisions due to data and important information inspection
- High speed due to the use of powerful caching systems
Disadvantages:
- Incompatibility with all network protocols
- Performance degradation due to additional processing requests
- Difficulty in configuring the proxy firewall
Next-Generation Firewall
According to Gartner’s definition, the Next-Generation Firewall is a type of DPI (Deep Packet Inspection) that is combined with additional functions such as encrypted traffic inspection, intrusion prevention systems, antivirus, etc. Providing a comprehensive solution for filtering threats has made the NG Firewall used by most businesses and complex networks.
Important features of the NGFW can be pointed to as follows:
Application awareness to identify running programs and ports. This makes the system resistant to various malware that is used to terminate running processes or hack ports.
User identity awareness to enforce rules based on identity. With this feature, systems, and users intending to access the system are identified.
Sandboxing for isolating codes associated with incoming packets. This capability makes decisions by adding code snippets to a sandbox environment and carrying out necessary operations regarding its behavior. Sandbox test results can be used as a criterion for deciding on granting network access.
So, considering these features, we understand that these firewalls are more complex than packet-filtering firewalls and have higher security levels.
Advantages:
- Easy access to the Firewall through the console
- Multi-layered protection of the system or network
- Easier management and updating of security protocols
Disadvantages:
- High resource consumption
- Slow speed
- The need for high expenses for installation and setup
Circuit-Level Gateway Firewall
This firewall operates at the fifth layer, or session layer, and inspects packets exchanged during a connection. If they have a desirable state, the connection between two networks is allowed, and afterward, the firewall ceases to monitor the connection.
The operation of this firewall is similar to a proxy firewall, and it examines the information exchanged during the handshake between two networks. This data found in the packets could signal harmful or dangerous data, allowing the firewall to act before the system becomes infected and reject it.
This firewall decides on the legality of connections using a series of security functions and helps create security between UDP and TCP by protecting and hiding information about the private network.

Advantages:
- Low implementation cost
- Easy setup and management
- Hiding private network information
Disadvantages:
- Does not filter individual packets
- Does not scan active content
- Lacks application layer supervision
NAT Firewall
The Network Address Translation (NAT) firewall allows multiple devices with different network addresses to connect to the internet using a single IP address, keeping the addresses of each hidden. As a result, hackers scanning the network cannot record specific details, and this protection of addresses should increase security against attacks.
This firewall also resembles a proxy firewall and acts as an interface between a group of computers and external traffic. In general, a NAT firewall only accepts incoming traffic when a device from the private network has requested it.
Although this firewall is not as effective as other firewalls, it has its own unique advantages, which prevent malicious data from infiltrating the private network’s IP address when placed at the router level.
Advantages:
- Cost reduction
- Private IPv4 addressing system
- Increased network flexibility
Disadvantages:
- High memory and CPU usage
- Difficulty in network troubleshooting
- Decreased network integrity due to NAT’s ability to change header values
Web Application Firewall
Just as previous firewalls are used to protect private networks, web application firewalls are responsible for protecting web applications from attacks and malware infiltrations. Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) are tasked with filtering, monitoring, and blocking traffic that is exchanged between a web application (or website) and the internet.
A web application firewall can be located in the host system or in the cloud and is available as a server plugin, cloud service, or network equipment.
While this firewall is also similar to a proxy, a proxy firewall protects the system using an intermediary, while a WAF is a kind of reverse proxy. Clients pass through the WAF before reaching the server, which keeps threats and risks away from the server.
Advantages:
- Analyzing the overall structure of a web application, including requests, URLs, and types of permissible data
- Utilizing artificial intelligence techniques and algorithms for behavioral analysis
- Possibility to customize security rules
Disadvantages:
- Heavy dependence on security rules and policies
- Need for high expertise and precision in defining rules
- The process of updating rules for each component is difficult
Types of Firewall Deployment Methods
Firewalls, depending on the needs of organizations, are deployed in three different methods, which we will review below:

1- Hardware-Based Firewalls
These firewalls use a physical device as a traffic router to track data packets and traffic requests before they connect to the system or server and block any detected malicious traffic. Most routers have firewalls and act as a gateway within the network environment. Since hardware firewalls don’t consume the processing power of a device, they are suitable for individuals or small organizations.
The main drawback of these firewalls is that they only protect devices behind the router, and their updates and installation require specific skills. Moreover, they are often vulnerable to internal attacks.
2- Software-Based Firewalls
A simple and common example of a software firewall is the Windows Defender Firewall program, which comes pre-installed in all Microsoft Windows operating systems. These firewalls control the traffic related to each system separately.
Installing software-based firewalls requires time and manpower and likely consumes significant CPU and RAM resources.
However, maintaining these types of firewalls can be somewhat challenging. Also, assuming that each device in the network may not be compatible with a specific type of software firewall, you would need to use several different firewalls to cover all devices. This can lead to wasting a lot of energy, cost, and time to achieve a stable and secure situation.
3- Cloud-Based Firewalls
These firewalls are also known as FaaS (Firewall as a Service) and work like the previous two methods, but they create a barrier between your cloud and the systems and networks connected to it.
The main advantage of FaaS is that its scalability with any organization is very easy. As needs increase, you can add extra capacity to the cloud server to handle larger traffic loads efficiently. Overall, these firewalls provide the necessary security environment for network architecture.
What is a Personal Firewall?
A personal firewall and a regular firewall differ only in terms of scale. A personal firewall typically protects only the system or server on which it’s installed and controls its inbound and outbound traffic. With this in mind, when firewall rules are to be applied to a single system, you have more freedom to create customized and personal rules.
So, when you need minimal protection and need numerous open ports for services like file sharing or printing, your system does not have to adhere to the general firewall rules that apply to systems on the network. On the other hand, creating stricter rules for a system or server that contains highly sensitive information prevents the creation of a series of exhausting processes for other systems on the network. In other words, by using a personal firewall, you ensure that the proverb “each to their own” also holds true for the systems on the network.

Why Should We Use a Personal Firewall?
With a personal firewall, you elevate the protection and security level of your system and owe this to the benefits you gift your system with a personal firewall.
A personal firewall:
- Blocks unauthorized hacker attempts to establish inbound or outbound connections and immediately informs the user.
- Allows the user to control the access of applications to the local network or the internet and see the necessary information about application connection attempts.
- Conceals the system by not responding to unwanted network traffic and prevents port scanning.
- Monitors applications that are listening to inbound connections.
- Monitors and regulates inbound and outbound user activities.
- Provides information about the destination server to which an application is attempting to connect.
- Controls inbound, outbound, and intrusion events to inform the user of individuals trying to access the system.
- Blocks hacking attempts or attacks.
Security Tips Related to Firewall
First of all, it’s better to mention that having a firewall does not necessarily protect you from all threats and attacks. There are numerous risks that can still affect your network, even with a firewall in place. Malware, ransomware, viruses, worms, spyware, spam messages, phishing, and Trojans are among the threats that can infect your system.
Clicking on a link in an email, installing malicious software, physical theft, information leaks, connecting a USB for tracking your activities, etc., are some issues that a firewall cannot counter.
However, the following points we will examine will help you maximize the security resulting from the proper use of a firewall:
- Update your firewall as soon as possible.
- If possible, enable the automatic update feature of your firewall.
- Use antivirus software.
- Limit accessible ports and hosts.
- Restrict inbound and outbound connections to a whitelist of IP addresses.
- Back up sensitive network data.
- Design and optimize specific network rules to provide the expected security protection. For example:
- Remove contradictory rules.
- Remove redundant and repetitive rules that reduce firewall performance.
- Eliminate errors and inaccuracies in firewall rules.
- Remove outdated rules to reduce system complexity.
- Update the rule list to stay in sync with new vulnerabilities.
- Monitor user access and allocate specific traffic to specific services.
- Regularly review firewall logs to identify any unauthorized intrusions from inside or outside the network.
- Manage all network firewalls centrally and in one place to ensure their proper functioning.
Conclusion:
Firewalls are an essential component of computer networks, and their proper and timely use reduces the likelihood of attacks and hacking of systems within the network. Firewalls come in various types, each filtering according to their structure and target scope, operating in their specific areas.
Thank you for staying with us until the end of the article. We hope that reading this article has been useful to you. If you have any questions or requests or need guidance, you can contact us by leaving a comment, and we will respond as soon as possible.
Frequently Asked Questions:
How does a firewall work?
A firewall acts as a barrier or gate between your system and another network, such as the Internet. In fact, a firewall monitors, controls, and filters the traffic intending to access your system.
What is the difference between a hardware firewall and a software firewall?
A hardware firewall is a physical device, like a router, that is placed between the network and the gateway. A software firewall is an internal component that operates through port numbers and applications.
Related posts:



