Hello, I am keleis Andre and I have been working in the field of cybersecurity for years. Today, let’s talk about the world of phishing and hacking. Phishing is a scary word these days, and the first and simplest way to combat it is to increase awareness and raise individual information in the field of the internet. A phishing attack is the same trick that helps cyber thieves and scammers collect personal information and credit card data for their evil purposes. But in response to the important question “What is a phishing attack?” we must say that it is a type of cyber attack to steal user information that is carried out through fake portals such as: email, SMS, audio files, and other similar cases.
This type of online fraud has emerged with the advent of online stores and payment of money through bank payment gateways, and are considered new methods of theft. In this article, we will fully and comprehensively review phishing attacks and ways to combat them. So stay tuned with SPY24 until the end of this article.
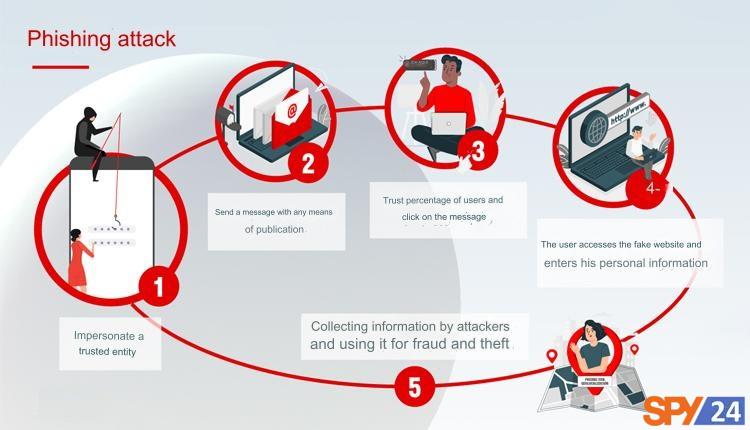
What is phishing?
If you pay attention, you will notice the close relationship between the words “Fishing” and “Phishing”. Both words have the same pronunciation and provide a similar meaning. The first word means fishing and the second word means a type of cyber attack. But what is the secret of the relationship between fishing and this type of attack?
In response, it must be said that a trap is needed during fishing in order to catch fish. Exactly in cyber attacks, under the name of phishing, there is also a need for a trap to lure victims. Now, this trap can be a fake email, a fake payment gateway, a fake website, SMS or message from an illegal source that has been created for fraud and theft.

The first report about this type of attack was registered in 2004 against a Californian teenager who was able to obtain important information from many users by creating a fake version of the America Online website. Among these sensitive data, it is possible to refer to the credit card information of the victims, which is a good way to withdraw money from their accounts. This type of fraud has also become very common in the world.
How Phishing Works
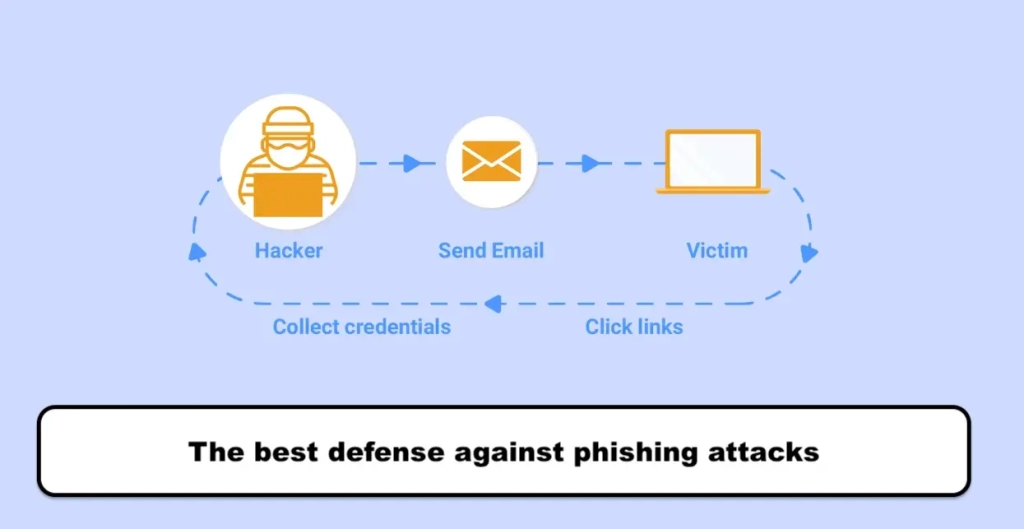
Now that we’re familiar with the terrifying concept of phishing, let’s talk about how these attacks work. The main element of phishing attacks is a message that is sent through channels such as email, social media, and other electronic communication devices. The phisher gathers information about the victim, such as their job, email address, age, date of birth, interests, and activities, by reviewing public sources. Then, they create a fake message that appears to be legitimate at first glance.
This message usually contains malicious attachments or links to malicious websites. The attacker tries to obtain sensitive information such as the victim’s username and payment information in any way possible and complete the attack.
One of the most common examples of phishing is sending a message (from any channel, whether SMS or email) by a hacker to a large number of people with a message like “Your password has been changed on such and such site or network. If this was not done by the account owner, please take the necessary security measures by visiting the link below.”

Now, any type of content can be included in these messages based on the creativity of the hacker. The important thing is the link that encourages you to click on it. When the victim clicks on it without intention or accidentally, they are directly transferred to a page that is exactly like the original website. Due to the very high similarity of the fake page to the original type (these fake pages are almost indistinguishable from the original type because hackers easily create fake pages by copying codes from the original source), in this step, many victims are simply fooled.
Now all you need to do is enter your information based on the fields on the page. All the data is sent to the hacker instead of being sent to the trusted and original source. If you pay attention, this type of cyber attack is much simpler and even more efficient than designing a complex algorithm to infect devices such as viruses or ransomware. That’s why any beginner can implement different phishing modes with a little training.
Therefore, one of the main reasons for the increasing trend of phishing attacks is its simplicity. Poverty and economic problems have forced many young people who have access to the internet and a regular system to do this.
Who is a phisher?
In the design of phishing traps, there is always a person behind the scenes who directs the attack, known as a phisher. If you consider phishing as fishing, the phisher is the fisherman or the one who sets a trap for the victims. Often, phishers do not have any special expertise or knowledge about what they are doing, and they only act to steal property and steal information by following some common steps.
Access to the Internet and a computer system can turn anyone into a phisher. The basis of this type of person’s work is copying. People try to deceive Internet users by imitating the workflow of various organizations and companies, as well as designing pages that are exactly the same as the original.

What are the characteristics of phishing attacks?
The most important feature of phishing attacks is their attractive design. For example, they claim that you have won an iPhone or a valuable prize, while they only want to encourage you to click. On the other hand, they tempt you to take action as soon as possible by creating a sense of urgency. It seems like you only have a few minutes to take advantage of a golden and unique opportunity.
Remember that phishing attacks contain fake hyperlinks and do not lead you to the desired page. Additionally, if you encounter an attachment in the text of an email that is unexpected, refrain from opening and viewing the attachment. Malware, ransomware, or other viruses may be waiting to greet you! Finally, do not even click on messages that come from an unknown sender and seem suspicious.
READ More: Instagram Hack with a Phishing (Creating a Fake Instagram).
Phishing Attacks Techniques
As mentioned earlier, phishing attacks usually start with a message. Therefore, most of the techniques used to trap victims are applied to these messages. The person who designs phishing attacks is actually playing with numbers. That is, by sending one type of message to thousands of people, they try to deceive the largest number of recipients. Therefore, always trying to make the message look real is one of the most effective ways to increase the success of the attack.
The first technique is to use an address with the least amount of difference from the original address. For example, if the address of the Google page is google.com, the attacker will use gooogle.com to make the message look more real. It should be noted that this technique does not only include the address of the link that is sent to you along with the message. The number that is used to send a text message or the email address that is used to send an email may also be changed in the same way.
The next technique is to make the message look authentic. This is done by the attacker reviewing the types of original messages and trying to design a message with a high degree of similarity. For this, the attacker may use a forged signature or seal of the organization.
Using the technique of pushing or pushing victims is very effective. By creating a sense of urgency and emergency in the message, the hacker tries to encourage people to fall into his trap. In this way, by making the message look urgent, for example, writing “You have 24 hours to …“, the victim is placed on a timer and as a result, it causes them to make more mistakes in the next steps and fall into his trap.
What are the types of phishing attacks?
It is important to know that titles such as: Instagram phishing, account phishing, bank card phishing, etc., all refer to the topic of abuse and theft of confidential information in the online space. In the following article, we will examine some of the most common types of phishing attacks together, which are as follows:

Email phishing
Most phishing attacks occur with email messages. The attacker performs the attack by encouraging the user to click on a malicious link or install malware and provide personal information. This is the most popular and frequent type of phishing attack, in which the attacker tries to forge the identity of the organization by registering a few fake domains and sending thousands of requests to it. There are several ways to identify phishing emails; the most important method is that the user should always check the email address and see if the sent message contains an attachment or link.

Spear phishing
In these attacks, the attacker usually has personal information about the victim and uses this information to make their message more effective so they can interfere with the victim’s activities. It can be said that these attacks also use a seemingly trustworthy source to deceive victims. With the difference that during it, an individual or a group of individuals are targeted; not that a few general messages are sent to several users in the hope that the user may be deceived! Human resources employees and IT managers are always the targets of these attacks; because they have higher and more extensive access in the organization.
Whaling phishing
These attacks target senior management and other prominent roles in the organization with confidential messages (such as tax returns) to use the information of these users to more effectively advance their attacks. Whaling phishing attacks are only effective and successful if the attacker tries harder than usual to deceive the whale (ambitious targets) and somehow convince him to disclose sensitive and valuable information. After success, attackers can use the target’s authority to attack other employees of the organization without causing suspicion.
Smishing and Vishing Attacks (voice phishing)
These attacks are carried out via mobile phones and by sending fake text messages and phone calls. The attacker pretends to be from the researchers of a company or credit institution and asks the victim to provide their payment card information. In smishing attacks, the attacker sends text messages with deceptive content, and in vishing attacks, deceptive content is provided to the victim via phone calls.
For example, a scammer may pretend to be an investigator from a bank or credit card company and inform the victim of a breach in their account. They may then ask the victim to verify their identity by providing their credit card details. They may even ask them to transfer their funds to a special (scam) account.
Clone Phishing
In clone phishing, the phisher modifies a legitimate and authentic email that has already been sent. They use the same email content and add a link similar to the website of that email to the content instead. The phisher claims in the email that this is a new or updated link to the previous link.
Pharming
In this method, the phisher targets a legitimate DNS (Domain Name System) and infects it, which effectively directs users to a fake website that the phisher has prepared in advance. This is the most dangerous type of phishing attack, because when the DNS is infected, it means that users have no control over it and cannot continue to protect their information.
What is the difference between phishing and pharming?
Although we said a little earlier that pharming is a type of phishing, its mechanism is different from phishing. The main difference between phishing and pharming is that phishing requires a human error from a user, but for pharming, only the user’s access to a legitimate site is sufficient; the same site that the phisher has made changes to its DNS to his advantage.
Whaling Phishing
Whaling is a type of spear phishing that targets high-profile and wealthy individuals, such as CEOs of large companies and important government officials.
Website Redirects
Website redirects occur when a user attempts to visit a website, and the redirector directs them to a different website address. Phishers focus on vulnerabilities in websites to install redirects or even send malware to users’ computers.
Typosquatting
Typosquatting redirects traffic from popular websites to fake websites that have a small misspelling in their name. Typosquatting is also known as brandjacking. Phishers use these domains to mimic the user interface of legitimate websites. Victims of this type of phishing are tricked into entering the wrong website address.
Watering Hole Attack
In a watering hole attack, phishers monitor users and identify the websites they frequently visit. Phishers look for vulnerabilities in these websites, and if they find any, they infect the website with malicious scripts to target users.
Phishing via Advertisements and Search Engine Results Pages
Another type of phishing that we will discuss here is phishing through paid advertisements. These fake ads take over domains that are for phishers. Phishers use typosquatting there and do intrusions on login pages through which they can steal user information.
These sites may even appear on the first pages of Google search or the first option after your search that appear on the page with the names of reputable companies. These sites are used as a means of phishing.
Malicious Applications
In some cases, phishers will use applications (programs) to transfer malware to your system and steal your important personal information. These applications typically have virtual wallets, account control, and other tools that deal with people’s bank and currency accounts.
WIFI phishing
In a WIFI phishing attack, the attacker can easily copy personal information from your mobile phone or personal computer and use it. Therefore, we should never use WIFI in public places. For example, the hacker can use malware to enter your mobile banking app and hack your account and password.
Phishing by the Fisherman
In this type of attack, fake social media accounts belonging to well-known organizations are used to trick users. Fake website addresses, simulated posts and tweets, as well as instant messages can all be used to encourage people to disclose sensitive information or download malware. On the other hand, criminals can also use data that people post on social media on their own to execute targeted attacks.
In this type of fraud, the attacker creates an account similar to a well-known brand and responds to users’ messages on social networks with content complaining about the brand in question. They then send a link to the user that leads to a malicious website, or they continue the conversation with them to get the user’s personal information.
10 Ways to Prevent Phishing Attacks
If you feel that your organization is at risk of phishing attacks, you can use these methods to minimize the chances of attack success and damage to your company.
1. Train and educate employees
In a world where phishing attacks are increasingly common, it is essential to train employees to understand the strategies of these attacks, identify phishing signs, and report suspicious incidents to the security team. Organizations should teach employees to look for trust indicators on websites before interacting with them and to make sure that security is taken seriously on those sites. (Most links do not have Https or a lock image next to the URL, which is a 95% indication of a fake page.)
2. Deploy email security solutions
New email filtering methods can help to prevent the spread of malware and other malicious programs. This way, all emails containing malicious links, attachments, and spam content can be quickly identified, blocked, and quarantined.
3. Monitoring and protecting endpoints
The increasing use of cloud services and personal devices in the workplace has led to an increase in the number of endpoints that may not be fully protected. Endpoint monitoring is essential for preventing security threats, remediating them, and responding quickly to at-risk devices.
4. Implementing phishing testing
By implementing phishing testing, security teams can assess the effectiveness of security awareness training programs. Even if you feel your employees know how to deal with suspicious messages, test them regularly to ensure they are prepared to face real-world attacks. As the threat landscape continues to evolve, so too must methods for combating cyber attacks.
5. Limiting user access to systems and valuable data
Most phishing methods are designed to deceive human operators. However, among all regular users, the accounts of privileged users are a more attractive target for cyber criminals. Therefore, limiting user access to sensitive systems and organization data helps prevent their leakage. Try to only give access to users who need it to perform their duties.
6. Check the content
It is best to check a part of the content (or the sender’s email address) on one of the search engines like Google. Perhaps someone has already been caught in this type of phishing and has shared it on the internet.
7. Use other tools
If you think the request to verify the information you have received for your accounts is valid and legitimate, it may be better not to click on the link that has been sent to you and use other tools to validate this request.
8. Update our browsers
Security issues are resolved in new versions of popular and popular browsers. Try to update our browsers every once in a while.
9. Enable two-factor authentication
One of the things that helps prevent phishing is to use two-factor authentication, which helps to secure your user account. So, we must definitely use two-factor authentication for social media accounts, such as two-factor authentication for Instagram. For a bank card, activate the second password from the bank.
10. Never share your private keys
Never share your private keys or recovery words. Also, make sure the buyer and seller you are exchanging any type of cryptocurrency with are legitimate and trustworthy, and be as obsessive as possible. The main difference between buying Bitcoin (and other cryptocurrencies) and buying with a credit card is that there is no recourse to pursue if a problem arises with Bitcoin, but this is not the case with credit card purchases. So, you should be more careful when making digital purchases than other purchases so that you don’t get caught in cryptocurrency phishing.
Install an anti-phishing toolbar
The Anti-Phishing toolbar is a layer of protection against phishing scams and is completely free. This toolbar provides easy search access for information about sites you visit and protects against phishing.
Most popular web browsers have anti-phishing toolbars such as Netcraft Toolbar, McAfee SiteAdvisor, Finjan SecureBrowsing, Bitdefender TrafficLight, and more. These types of toolbars are quickly executed on the sites you visit and compare them to a list of known phishing sites.

How to deal with a phishing attack?
When you are the victim of a phishing attack, take a few deep breaths and clear your mind before reacting. Remember that phishing comes in many forms and does not necessarily mean that your identity has been stolen.
1. Disconnect your device
If you think you have downloaded malware, disconnect your device from the internet immediately. This will help prevent the malware from spreading to other devices and infecting your personal information.
2. Create a backup
Once you have successfully disconnected from the internet, it is time to create a backup of your files so that they can be recovered if they are deleted. Protect sensitive information and documents, as well as valuable files such as family photos and any irreplaceable content. You can create a complete backup of your files using an external hard drive or a cloud storage service such as DropBox or Google.
3. Change your user information
If you accidentally clicked on a malicious link, were directed to a fake and fraudulent website, and entered your important information there, immediately change your username and password. In this form of phishing, the attacker poses as a social media platform to obtain the user’s important information related to their other accounts. So take the time to change all of the important information you entered on the fraudulent website.
4. Scan your system
Get to work and scan your system as soon as possible to scan it completely for any malware or virus. If you don’t have much information in this area, you can also ask a qualified professional for help. If you already have an antivirus software installed on your device, simply run the program once and see what information it provides you about the status of the system. This scan may take a while; be patient and try not to use your device until the scan is complete.
Conclusion:
As we rely more on new technologies, we are exposed to new threats and dangers. In recent years, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, we have seen a surge in the use of online services around the world. This has led to an increase in the theft of user data when using online and internet services.
Statistics all over the world also speak of the staggering growth of online theft. If you want to avoid being a victim of cyber attacks, the only solution is to increase your knowledge and understanding of how to use online services correctly.
In this article, we have thoroughly reviewed one type of cyber threat called phishing. We have also explained the countermeasures against it and even the techniques that hackers use to deceive victims. We hope that by reading this content, you will be able to better protect your property and privacy.
What is Phishing?
Phishing is a type of online fraud that aims to steal users’ personal information such as bank account information, credit card information, passwords, etc. Phishing is often done through emails or anonymous messages that persuade victims to click on links and enter their sensitive information or are threatened to be exposed if they do not click on the link and reveal the information.
How can I avoid suspicious emails?
Never click on suspicious links in emails. First check the link address to make sure it connects to a legitimate site.
Never download any text file or attachment unless you are completely sure that it was sent from a secure sender.
Filter suspicious emails. Improve your email filter settings to identify more emails as spam.
Do not respond to emails that request immediate submission of sensitive information such as credit card numbers and delete them.
Use an encrypted email address to contact your bank and other sensitive sites.
What is Phishing in Banking?
Phishing refers to fraudulent emails that trick recipients into sharing their personal, financial, or security information about their bank accounts.